

Shares of electricity, heat and transport in energy
consumption
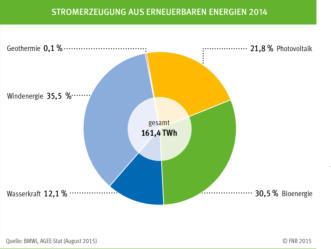
The below graph (FNR) shows the shares opf different
renewables in overall renewable electricty production:

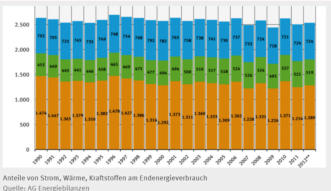
Source: Umweltbundesamt
Source: Frankfurt School of Finance & Management

Our Services
Renew-Sources informs on all aspects of nenewable energies, we organise Workshops and support in: • identifying the chances of investing in renewables for the client, • developing concepts for bioenergy plants and feedstock supply, • preparing feasibility studies, • ………….. Please contact us for further information:.
Renewable Energies:
The German Experience:
The “Energiewende” in Germany is the most fundamental
transition process since Germen Unification. It shows
significant impact on the overall economy, landscape
orinary citicens life and the energy sector itself.
The “Energiewende” adresses - and must do so in order to
achieve significant impacts in climate protection - not only
electricity production and consumption (which is about
30% of overall energy consumption in Germany), but
heating and transport.
German Energy and Climate Policy is mainly focusing on the
electricity sector. The Renewable Energy Act (EEG)
significantly increased the share of renewable electricity
form 7 % in 2000 t an actual share of 32,5 % end 2015. Till
2025 the share of renewable electricity shall reach between
40 and 45 % ant till 2025 between 55 and 60 %.
After electricity based on wind Bioenergy provides about 30
% of renewable electricity.
Different from Wind and Solar Biomass can provide
electricity either as base-load or peak load electricity.
Biomethane can use the existing natural gas grid and can
be transported to decentral CHPs nearby the place of
usage.
Although there is no other such renewable available the last
adjustment of the Renewable Energy Act EEG-2014 will
result in a standstill in the electricity production from
biomass. From 2020 onwards existing biomass facilities will
quit production.
In Germany the “Energiewende” results in a fundamental
change of the structure of energy production. In the past
power plants were build close to the centers of electricity
consumption. Nowadays production facilities are
established in those regions with good conditions for that
kind of renewable electricity production (e.g. Wind offshore,
solar in the south).
Private consumers cover the highest share in the costs.
Consumer costs are estimates at 28 Billion Euro/a resulting
in an increase of the annual electricity bill of the avearge
household by about 270 Euro.
A fundamental change inside the electricity sector is
ongoing, resulting in a fast loss in significance of the large
electricity companies (E.ON, RWE, ENBW, Vattenfall).
More and more small producers substitute the large power
plants.
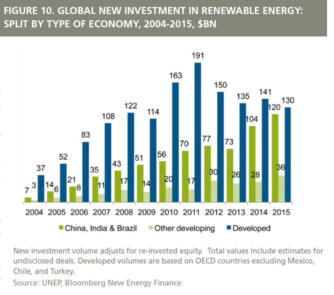
On a World-Wide level 2015 “was a signal year for
renewable energy because, for the first time, investment in
developing economies out-weighed investment in
developed countries. Commitments by the developing
world amounted to $155.9 billion, up 19% to a new record,
while those by the developed world slipped 8% to $130.1
billion.” (Source: Frankfurt School of Finance &
Management)


© Renew-Sources 2018





















